7 ecommerce kpis you need to be tracking
E-commerce KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are measurable metrics used by online businesses to assess their performance, identify areas for improvement, and track their progress toward achieving specific goals. These KPIs help businesses understand their overall health, customer behavior, and financial performance. Here are some essential e-commerce KPIs and why you should track them:
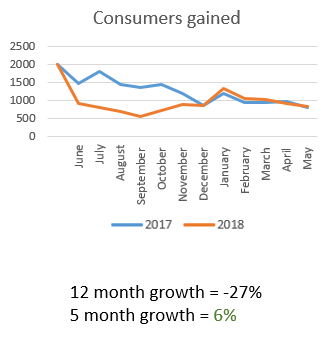
New Customers Acquired
A fundamental metric for any business is the number of new customers being recruited. Continuously identifying new opportunities for customer acquisition is key. Your marketing budget has likely been approved, and your company expects a return on that investment, so it's critical to monitor the cost per acquisition (CPA) of each new customer. After acquisition, it’s important to integrate them into an email welcome program to encourage repeat purchases.
Example: A retailer saw a 6% year-over-year (YOY) increase in new customers, but there was a significant drop in the early months, with recovery occurring in the last five months of the year.
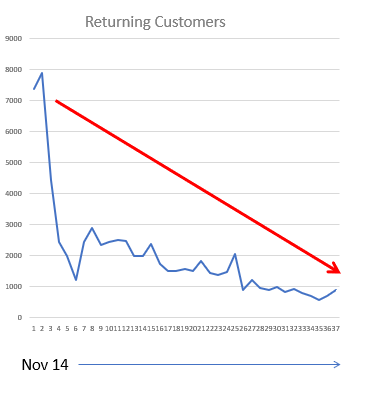
2. Returning Customers
Are your customers continuing to engage with your brand? This metric should either remain stable or increase as you acquire new customers and work to retain them. If you notice a drop in returning customers, it could indicate underlying issues with your products or services. For example, a price increase on delivery charges may cause customers to look elsewhere.
Example: This retailer experienced a sharp decline in returning customers, which was traced back to stock issues and product availability.
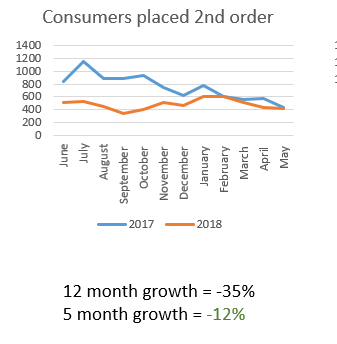
3. Customers Making Second Purchases
Encouraging customers to make a second purchase is often challenging, depending on the type of product you sell. Once a customer makes their first purchase, it’s important to engage them with relevant content and offers to maintain the relationship. This could include sharing your brand’s story or offering upsell/cross-sell opportunities for complementary products.
Example: This retailer faced difficulties in getting customers to make a second purchase online, as many were going into physical stores for subsequent orders.
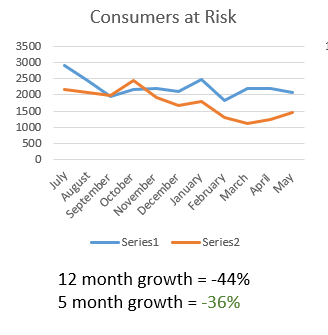
4. At-Risk Customers
While focusing on new customer acquisition and repeat purchases, it's also crucial to monitor customers who haven’t shopped with you in a while. These are your "at-risk" customers. Every business will have a different purchase cycle, so it’s important to define what "at risk" means for your business and track this metric regularly. Ideally, this number should decrease over time as you implement strategies to re-engage these customers.
Example: This retailer identified a high number of at-risk customers. By analyzing their purchase behavior, I developed a strategy to reduce this number, improving customer retention over time.
5. Lapsing Customers
Lapsing customers are those who were once active but have stopped purchasing. Identifying and tracking lapsing customers is crucial, as it allows you to implement retention strategies before they completely churn. Understanding your customer segments is vital here, as some customers may lapse due to seasonal promotions or one-time discounts.
Example: This retailer saw a sharp spike in lapsing customers following a giveaway campaign. While the campaign drove 10,000 new customers, 88% never returned to make a second purchase.
6. Conversion Rate
The website conversion rate is a key metric for any e-commerce business. It’s the ratio of orders placed to the total traffic visiting the site. The conversion rate can vary significantly across industries, so it's important to benchmark this figure for your specific business type. For example, fashion retailers might typically see conversion rates between 4-5%, while other industries may experience higher rates due to customer loyalty.
Example: This business had a typically high conversion rate but saw a dip due to stock issues. Once the problems were addressed, the conversion rate improved significantly.
7. Traffic by Channel
Tracking traffic by channel might not always be a priority for some businesses, but I find it very useful. When set up properly, it allows you to evaluate the performance of each marketing channel and understand what’s driving growth and what’s not. For larger businesses, this KPI provides insight into the main growth channels—direct, organic, and email traffic.
Example: This business faced a decline in both email and direct traffic due to regulatory changes and years of underinvestment. The one bright spot was organic search, which, with proper investment, showed a significant increase in qualified traffic.
In Conclusion
Every business should track key KPIs to ensure it’s growing and addressing any identified issues. By focusing on these 7 KPIs, you’ll gain a clear understanding of how your e-commerce business is performing.
It’s also worth noting that while these 7 KPIs are crucial, there are other important metrics to consider, such as the number of orders placed, units sold, Average Order Value (AOV), and revenue. These additional metrics provide a more comprehensive view of your performance.
challenges embedding data science in a business



07592629885
get in touch

